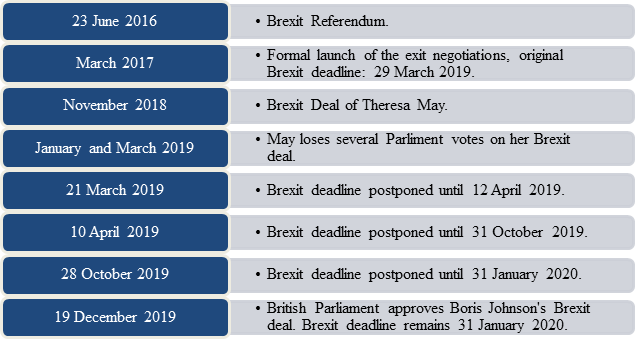
The last year of the old decade brought so many twists and turns on the subject of Brexit that one could easily lose track. Hence, our first blogpost of the new decade will shed some light on the current Brexit situation and the next steps currently planned by British and European politicians. As always, we will focus in particular on the effects on the financial market.
Current Situation: What Will Happen Now?
Since the British Parliament approved Johnson´s Brexit deal in December 2019, the UK will leave on 31 January 2020. An 11-month transition phase will then come into force: the UK will remain in the EU single market and the customs union until the end of 2020. During this period everything will remain mostly the same for the time being.
During the transition period, the EU and the UK will have to reorganise their relations with each other, with future economic relations as well as security and defence cooperation being key issues. First of all, a comprehensive Free Trade Agreement is to be concluded, which can above all prevent customs duties at the borders. But other economic areas, such as the financial market in particular, must also be regulated, either as part of the Free Trade Agreement (which would be unusual from a legal perspective) or through a separate agreement.
11 months are a short time and one may have doubts as to whether this time will be sufficient. The European Commission is already considering equivalence assessments for the financial market. However, there will be not ONE equivalent decision (see here) for an earlier analysis of the equivalence principle of the EU). There are currently around 40 equivalence areas which need to be assessed in each case. Most equivalence decisions provide for prudential benefits, some provide for burden reduction and some can lead to market access. There will also have to be close cooperation between the UK and EU financial supervisory authorities. During the assessment process the EU will look at UK legislation and supervision and will take a risk-based approach – as for all other third countries. This means that the higher the possible impact on the EU market, the more granular will the assessment be conducted. In case the UK will stick with the current EU regulation, this will be an easier task. But as soon as the UK will break new ground to make the UK financial market more attractive the impact on the equivalent status will need to be considered.
It can be assumed that the German Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (Bundesanstalt für Finanzdiensteistungsaufsicht – BaFin) and the other European financial supervisory authorities will monitor the negotiations regarding a financial market agreement very closely during the transition phase and will adapt and communicate their intentions for action accordingly.
To Be Continued
Although a hard Brexit has been avoided, there will still be uncertainties about future relations between the EU and the UK. Financial market participants should follow the negotiations between the EU and the UK closely and not rely on the fact that a financial market agreement can be concluded successfully in the short transition period.

